Core technology: Composition development technology
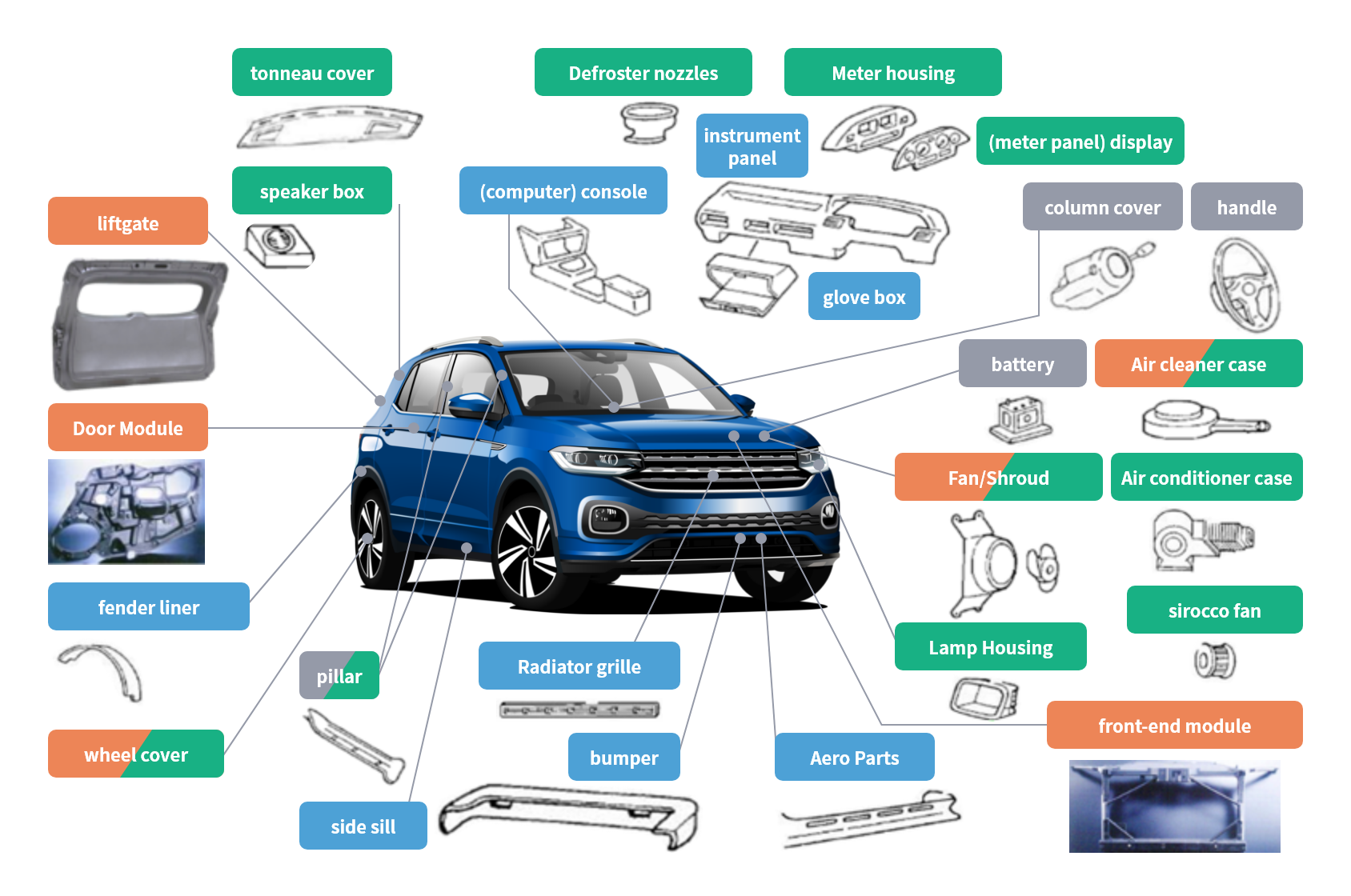
Polypropylene composites have a wide range of applications in industrial material components that require high strength, high impact strength, and durability.
In the automotive field, in particular, the need to "reduce weight" ⇒ "improve fuel/electricity costs" ⇒ "reduce CO2 emissions" has led to the application of this material to bumpers, instrumental panels, door trims, and under-hood parts, and more recently to back doors, fenders, and other external automotive parts that previously used metal or engineering plastics.
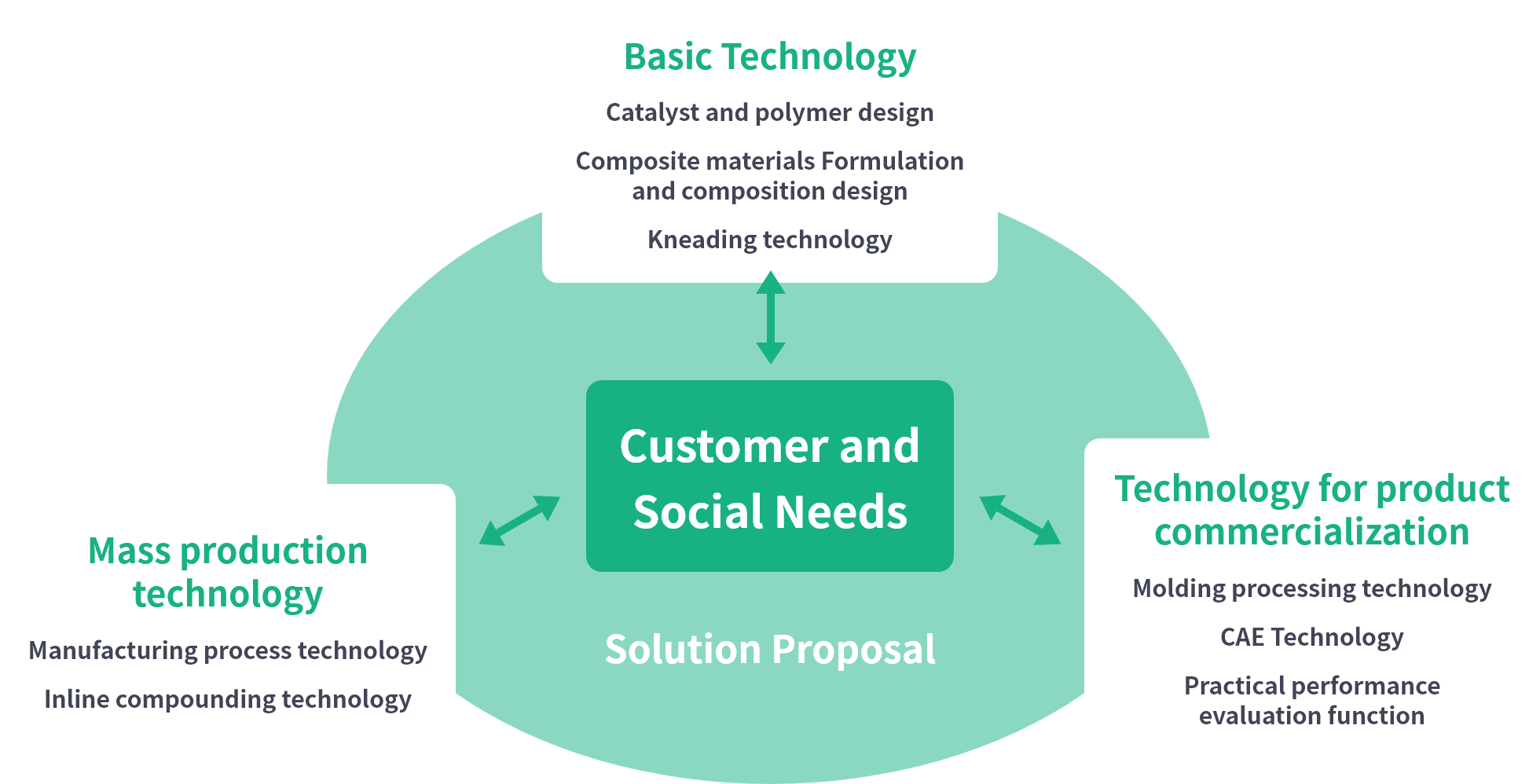
In the development of polypropylene composite materials, we will continue to propose and provide high-performance, high-quality materials that meet the needs of customers and society and reduce environmental impact through our original fundamental, commercialization, and mass production technologies.
Providing high-performance, high-quality materials
Contributing to Reduction of Environmental Impact
Polypropylene Composites: Components and Functions
| Composite Ingredients | Component Example | function |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | HOMO polymer, Impact copolymer | Molding processability, General mechanical properties |
| Rubber | Thermoplastic elastomer | Impact resistance, Paint adhesion, etc. |
| Inorganic filler | Talc, Glass fiber, Carbon fiber, Mica, Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) | Rigidity, Strength, Heat resistance, Dimensional stability, etc. |
| Addition agent | Antioxidants, Light stabilizers, UV absorbers, Lubricants, Nucleating agents, Antistatic agents | Thermal stability, Weather resistance, Antistatic properties, Scratch resistance, Improved physical properties, etc. |
Polypropylene Composites Application Examples
- PP alone
- Filler Reinforcement
- Rubber and
filler reinforcement - Glass Fiber
Reinforced